





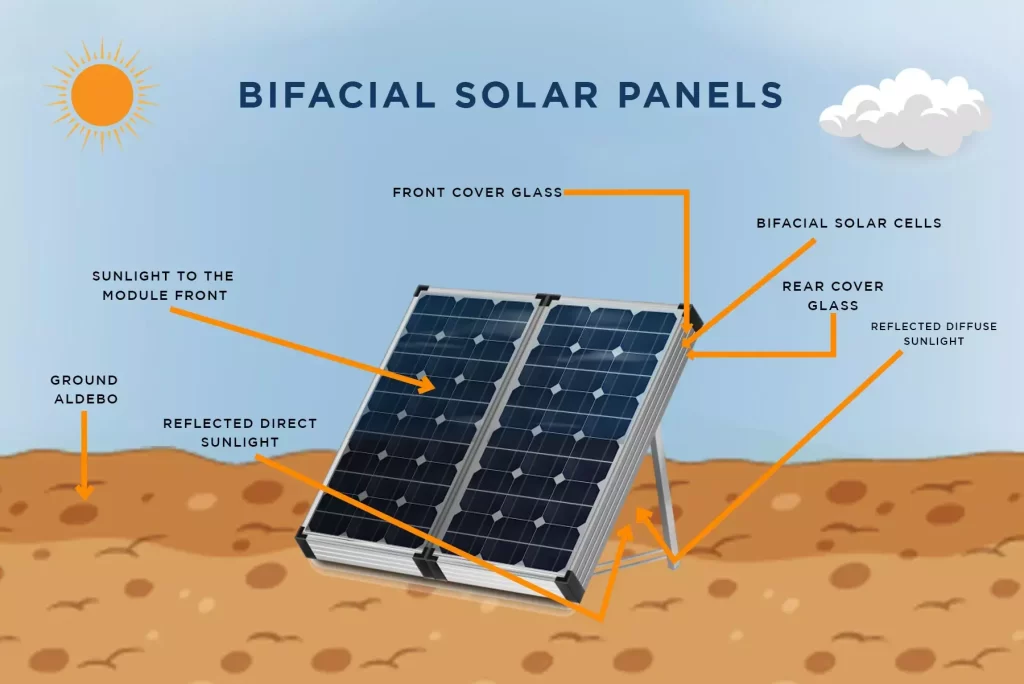
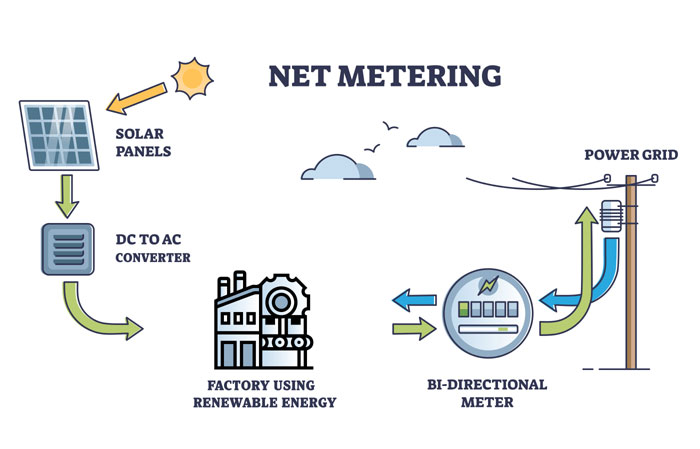





















A solar furnace is a device that concentrates the sun's energy to produce extremely high temperatures, typically used for industrial processes such as melting metals, glass production, and solar thermochemistry. With the increasing demand for renewable energy and energy efficiency, solar furnaces are becoming increasingly popular as an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional fossil fuel-powered furnaces.
In this comprehensive guide, we will cover everything you need to know about solar furnaces, including their history, design, and applications.
The concept of solar furnaces can be traced back to the ancient Greeks, who used magnifying glasses to focus the sun's energy to start fires. In the 19th century, the French engineer Auguste Mouchout developed the first solar-powered steam engine, which was based on the principle of solar concentrators.
The first solar furnace, as we know it today, was built in the 1930s by the French scientist Henri Becquerel. It was a large parabolic reflector that concentrated the sun's energy onto a single point, reaching temperatures of up to 3,000 degrees Celsius. Since then, solar furnaces have been used for a variety of industrial processes and scientific experiments.
Solar furnaces are typically made up of several key components, including a reflector, a concentrator, and a receiver.
The reflector is the primary component that captures the sun's energy. It is usually a large parabolic dish made of reflective material, such as aluminum or glass, that focuses the sun's rays onto a single point. The size of the reflector can vary greatly, ranging from small laboratory models to large-scale industrial furnaces that cover several acres.
The concentrator is the component that concentrates the sun's energy onto the receiver. It is usually a lens or a mirror that focuses the light from the reflector onto a small area. The concentrator is usually placed at the focus of the reflector, where the sun's energy is the most intense.
The receiver is the component that absorbs the sun's energy and converts it into heat. It is usually a metal rod or a small chamber that is placed at the focus of the concentrator. The receiver is usually made of a heat-resistant material, such as tungsten or molybdenum, to withstand the extreme temperatures generated by the solar furnace.
A solar furnace consists of a series of mirrors and lenses that are designed to collect and focus sunlight onto a single point. This point is typically located in a receiving tower, where the concentrated sunlight is used to heat a fluid or solid material. The heated material then transfers its heat to a heat exchanger, where it is used to produce hot water or steam.
The mirrors and lenses that make up a solar furnace are carefully positioned and adjusted to ensure that the maximum amount of sunlight is captured and focused onto the receiving tower. This is accomplished through the use of a computer-controlled tracking system that automatically adjusts the angle and position of the mirrors and lenses to follow the sun as it moves across the sky.
There are many benefits to using a solar furnace, including:
Despite its many benefits, there are some drawbacks to using a solar furnace, including:
Solar furnaces have a wide range of applications, including:
In conclusion, the Solar Furnace is a remarkable piece of technology that harnesses the power of the sun to reach extremely high temperatures. It uses mirrors and lenses to focus the sun's rays into a single point, which can reach temperatures up to 3000°C. This makes it an extremely efficient and environmentally friendly source of heat, as it does not rely on fossil fuels. The Solar Furnace has a wide range of applications, including scientific research, materials testing, and even industrial production. Its ability to produce such high temperatures has made it an important tool in many fields, and its use will likely continue to grow in the future.
Solar PV plants are also a great solution to offset the fossil fuel based electricity consumption for industrial purposes, switch to solar with Waaree Energies. Connect at waaree@waaree.com or call at 18002121321
you can also read: Solar Water Heater: The Comprehensive Guide